Leather sector supply chain is complex and dynamic. Increasing product complexity, out-sourcing and globalization in leather sector of Bangladesh are the reasons that have enhanced the risk in supply chains and shifting around supply networks. Procurement & Supply Chain professionals need to identify and manage risks from a more diverse range of sources and contexts. In the past, when shoe and leather goods were manufactured in-house, materials sourced locally and sold direct to the customer, risk was less diffused and was easier to manage. With the advent of increased product complexity and outsourcing of supply networks across international borders, risk is increasing, and the location of risk has shifted through complex changing supply networks.
What is Supply Chain Risk?
Supply risk is defined as the probability of an incident associated with inbound supply from individual supplier failures or the supply market occurring, in which its outcomes result in the inability of the purchasing firm to meet customer demand or cause threats to customer life and safety
What is Supply Chain Risk Management?
Supply chain risk management is the coordinated efforts of an organization to help identify, monitor, detect and mitigate threats to supply chain continuity and profitability.
Threats to the supply chain include cost volatility, material shortages, supplier financial issues and failures and natural and manmade disasters. Supply chain risk management strategies help an organization foresee potential issues and adapt to both those risks and unforeseeable supply chain disruptions as quickly and efficiently as possible.
Why is supply chain risk management Important?
- Risk management stimulates many supply best practices.
- Risk management generally improves supply chain partner relationships
- It provides visibility of supply chain-wide risk,
- The reality of soft risk—risk that is difficult to measure—and its unintended Consequences in business management.
- Every business faces the balance point of risk and reward.
Risk and Reward Analysis
A risk-reward analysis is a very simple tool which can help to assess the risk and reward profile of completely different options. The template works by having risk plotted along one axis and reward along the other. The diagram divided the template into four sections to show you how to interpret the information.
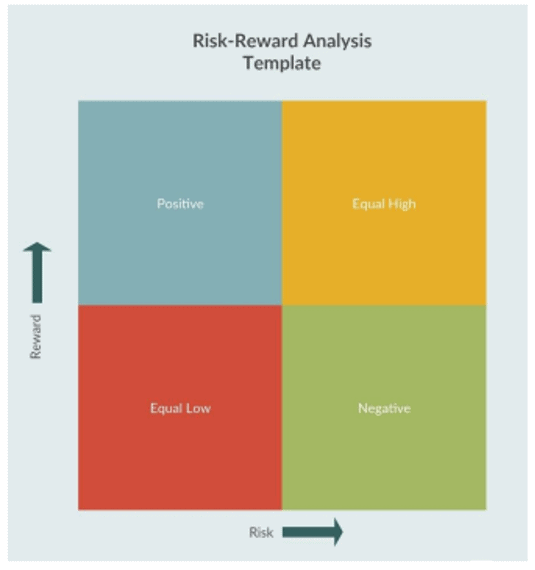
Source: APICS
The four categories from the diagram above are as follows:
- Equal Low: where risk and reward are both proportional and low. This risk can be taken.
- Equal High: where risk and reward are both proportional and high. Organization should take decision before taking this risk in line with its risk appetite. Action should be taken to reduce likelihood of the risk
- Positive: represents a positive risk-reward balance, where a higher return can be achieved with limited risk. This risk is worth taking.
- Negative: represents a negative risk-reward balance, where a low return is the reward for taking on a relatively high risk. This kind of risk should be avoided.
(continue…)
Author
Sheikh Nafiz Ahmed
MBA II Certified Supply Chain Analyst II
Experienced Leather Sector Supply Chain Professional



